By: Team T12-3 Since: Sep 2018 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Features
- 3.1. Viewing Help
- 3.2. Adding a Task
- 3.3. Adding a Recurring Task
- 3.4. Editing a Task
- 3.5. Deleting a Task
- 3.6. Archiving a Task
- 3.7. Viewing Archived Tasks
- 3.8. Viewing All Tasks
- 3.9. Viewing Overdue Tasks
- 3.10. Viewing Tasks Due Today
- 3.11. Viewing Tasks Due This Week
- 3.12. Viewing Tasks Due This Month
- 3.13. Viewing Tasks in the Order of Deadline Date and Priority
- 3.14. Sorting Tasks by Deadline Date and Priority
- 3.15. Finding Tasks by Name
- 3.16. Filtering Tasks by Tags (Inclusive)
- 3.17. Filtering Tasks by Tags (Exclusive)
- 3.18. Generating Academic Calendar
- 3.19. Adding a Category
- 3.20. Adding Tags to Categories
- 3.21. Clearing a Category
- 3.22. Deleting a Category
- 3.23. Renaming a Category
- 3.24. Displaying Category Tags
- 3.25. Displaying Today’s Progress
- 3.26. Displaying This Week’s Progress
- 3.27. Displaying Previous Commands
- 3.28. Undoing Previous Command
- 3.29. Redoing the Previous Undo Command
- 3.30. Clearing Schedule Planner
- 3.31. Exiting the App
- 3.32. Saving the Data
- 4. Command Summary
- 5. Possible Questions
1. Introduction
This User Guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough for new-users of the Student Schedule Planner (SSP). This walkthrough includes instructions on how to install the latest version of java, as well as downloading and running the SSP application.
Student Schedule Planner (SSP) is a desktop application created by Team T12-3. It is a planner customised for university students, and it aims to help university students manage their time effectively.
SSP incorporates features that streamline the creation, organisation, and finding of tasks. In addition, it allows the user to keep track of the current academic week, and has a progress tracking feature, which displays the user’s progress.
Instead of utilising a conventional Graphical User Interface(GUI). SSP is optimised for users who prefer typing out their commands. This application has the potential to be much faster than regular planner applications, especially for users who are proficient in typing. Move on to the Section 2, “Quick Start” to get started.
2. Quick Start
-
Install Java
9if you do not yet have it installed. It is available here.The application may not run correctly on Java 10or Java11. -
Download the latest
studentscheduleplanner.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder that you want to use as the home folder for your planner.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
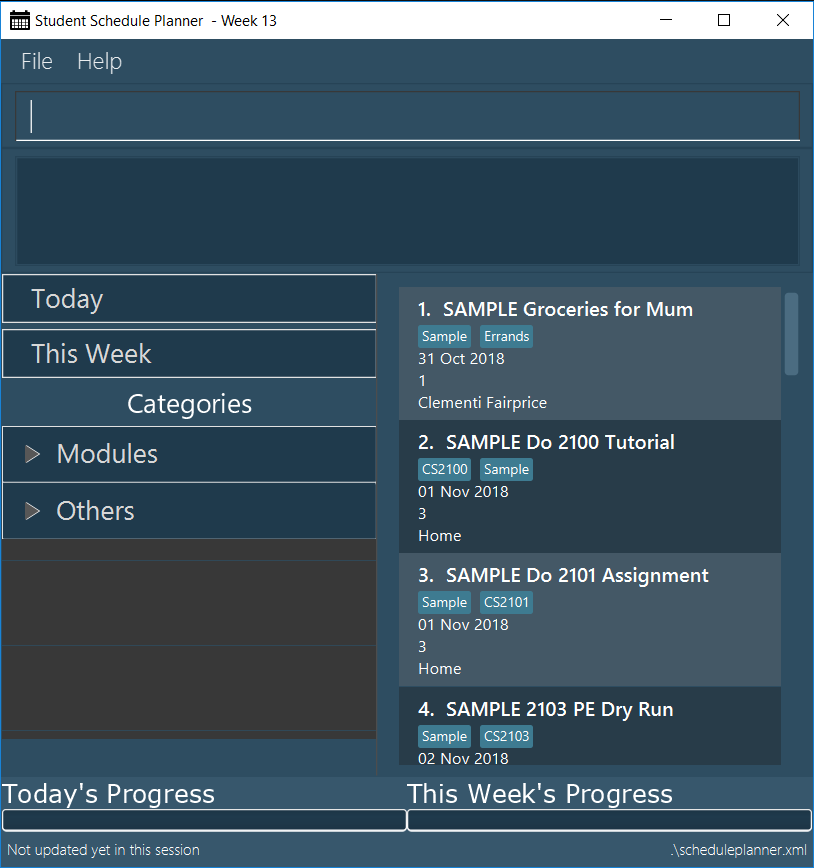
-
Type a command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Refer to Section 3, “Features” for details of each command.
3. Features
Understanding the command format
-
Parameters can be in any order:
n/NAME d/DEADLINE
d/DEADLINE
n/NAME is also acceptable.
-
Words in
UPPER_CASErepresent parameters to be entered by the user:
add n/NAME
n/NAME represents the task name which the user inputs, such as n/CS2103 Tutorial.
-
Items in square brackets are optional:
n/NAME t/[TAG]
The parameter t/[TAG] is optional, which means n/CS2103 tutorial
t/CS2100, and n/CS2103 tutorial are both valid commands.
-
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times:
t/[TAG]…
Allows for multiple tags to be input: t/tutorial,
t/tutorial t/CS2100 etc.
Please take note that naming is case-sensitive in Student Schedule Planner. For example, cats and Cats are
considered different. This applies to task, tag as well as category. Only find and filter commands
are case-insensitive for keywords.
|
3.2. Adding a Task
Add a task to the schedule planner.
add n/NAME p/PRIORITYLEVEL t/[TAG] d/DEADLINE v/VENUE
Example:
add n/exam p/3 t/CS3241 d/101018 v/mpsh1
Adds a task named exam with priority level 3,
tag CS3241 and deadline of 101018 , venue at mpsh1.
The priority level must be a number between 1 to 3, where 3 denotes highest priority.
Duplicate tasks are not allowed in Student Schedule Planner; two tasks are considered identical if they
have same name, deadline date, tags, and venue. If two tasks have same attributes except for priority,
they are still considered as identical.
Please take note that task name is case-sensitive. For example, task name study and Study are
considered different.
|
| The priority value must be a number between 1 to 3, where 3 denotes highest priority. |
| As we have implemented auto-sorting, if you add a task, it might get reordered in the task list. For more details about auto-sorting, please refer to Section 3.14, “Sorting Tasks by Deadline Date and Priority” |
| Name, Priority, Deadline, and Venue fields are compulsory, and therefore required for every task. Tags are optional. |
When you add tasks with new tags (tags that have not been added to any existing categories),
these tags will be automatically added to default category Others. For details about Category and Tags, refer to
Section 3.19, “Adding a Category” and [Adding a Tag to a Category].
When you add new tasks with new tags (tags that have not been added to any existing categories),
these tags will be automatically added to default category Others. For detailed guide about category and tags,
please refer to Section 3.19, “Adding a Category” and [Adding a Tag to a Category].
|
3.3. Adding a Recurring Task
Add tasks that occur in regular intervals.
repeat r/REPEATS i/INTERVAL n/NAME p/PRIORITYLEVEL t/[TAG] d/DEADLINE v/VENUE
Example:
repeat r/4 i/7 n/CS2103T Tutorial p/3 t/Tutorial d/111018 v/COM1-0210
Adds 4 tasks named CS2103T Tutorial with priority level 3,
tag Tutorial, venue at COM1-0210, and deadlines on the 11th October 2018, 18th October 2018, 25th October 2018, and 1st November 2018.
The diagram below illustrates the SSP before and after the above command was entered:
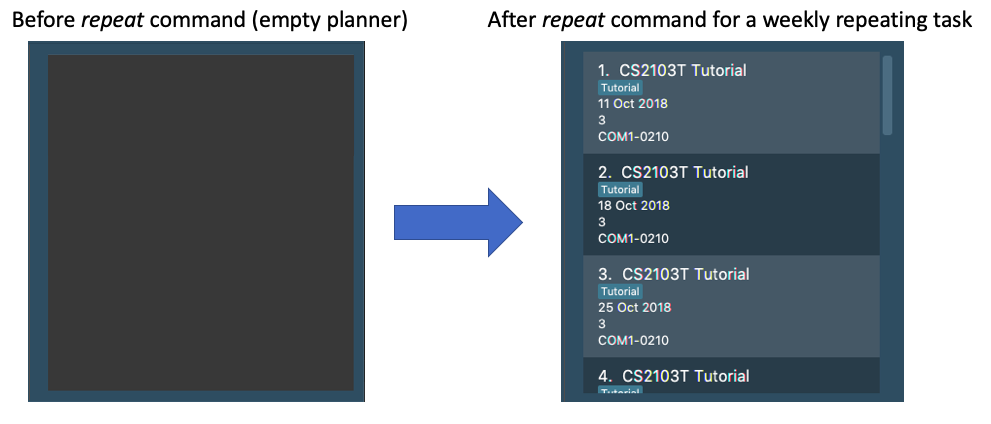
The number of repeats should be a positive integer (≥1). Setting the repeat as 1 has the same
effect as using the add command.
The number of repeats should be an integer that is greater or equals to 1. Setting the repeat as 1 has the same effect as using the add command.
|
| Use this command to schedule tasks that you carry out regularly. |
| The maximum number of repetitions is 15. |
| Tasks whose deadlines go beyond 2099 will have their deadlines set to the 21st century instead. For example, a task created by the AddRepeatCommand that with the deadline on 1st January 2101 will instead have the deadline set to 1st January 2001 instead. |
3.4. Editing a Task
Edit an existing task in the schedule planner.
edit INDEX n/[NAME] p/[PRIORITYLEVEL] t/[TAGS]… d/[DEADLINE] v/[VENUE]
Example:
edit 3 p/1 d/121019
The task at index 3 will have it’s priority value changed to 1 , and its deadline is changed to
121019.
INDEX refers to the number shown beside each task name in the displayed task list. Refer to the task
according to its index number.
The INDEX must be a positive integer (≥1)
The INDEX refers to the index number shown in the displayed task list. Refer to the task according to the index number.
The INDEX must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
| At least one of the optional fields must be provided. Existing values of provided field will be updated to the input values. |
Duplicate tasks are not allowed in Student Schedule Planner; two tasks are considered identical if they
have same name, deadline date, tags, and venue. If two tasks have same attributes except for priority,
they are still considered as identical.
Please take note that task name is case-sensitive. For example, task name study and Study are
considered different.
|
As we have implemented auto-sorting, if you edited date or priority, the task might get reordered in the task
list. For more detailed guide about auto-sorting, please refer to Section 3.14, “Sorting Tasks by Deadline Date and Priority”
|
Existing tags of a task will be removed when its tag is edited. If input is
edit 3 t/project, then the resulting tag(s) of task 3 will be project only.
|
To remove all tags of an existing task e.g for task with index number 3, you can type edit 3 t/, all the
tags of the task of index number 3 will be removed.
|
3.5. Deleting a Task
Delete the specified task from the schedule planner.+
delete INDEX
Example:
delete 3
Task with index 3 will be deleted from schedule planner.
The INDEX refers to the index number shown in the displayed task list. Refer to the task according to the index number.
The INDEX must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
INDEX refers to the index of the task in the displayed task list. Refer to the task according to its index
number.
The INDEX must be a positive integer(≥1)
Use the list command to find out the index of the task to be deleted.
|
3.6. Archiving a Task
Archives the specified task from the schedule planner. Once a task is archived, it will be hidden from task list. You can
view archived tasks in archived task list using listarchived command. For detailed guide regarding
viewing archived tasks, please refer to Section 3.7, “Viewing Archived Tasks”.
archive INDEX
Example:
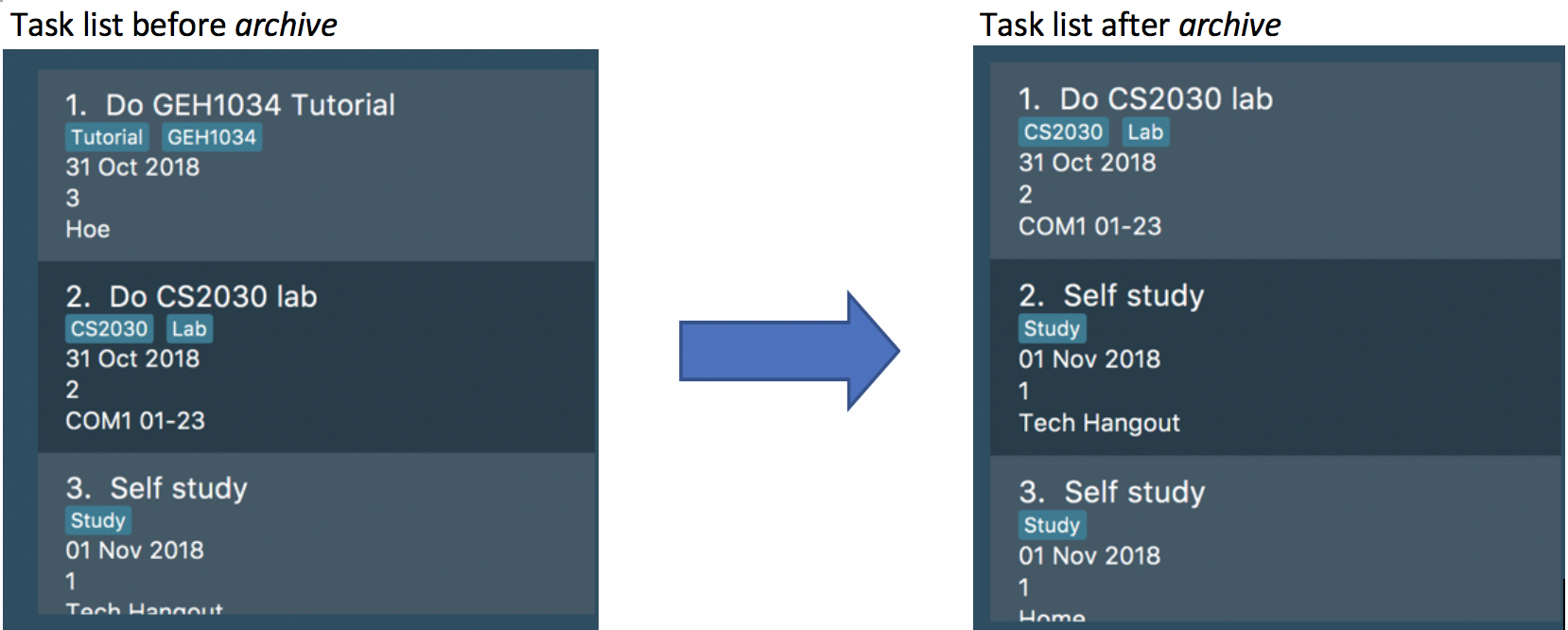
archive 1
Task with index 1 is removed from the task list.
Below is the partial screenshots of task list before and after executing the archive command.
The INDEX refers to the index number shown in the displayed task list. Refer to the task according to the index number.
The INDEX must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
INDEX refers to the index of the task in the displayed task list. Refer to the task according to its index
number.
The INDEX must be a positive integer(≥1)
Use the listarchived command to find out the index of the task to be archived.
View Section 3.7, “Viewing Archived Tasks” for detailed guide.
|
| Any archived tasks with deadline date earlier than 2 weeks before current date will be deleted from schedule planner when the application relaunches. |
3.7. Viewing Archived Tasks
List all archived tasks.
listarchived
Example:
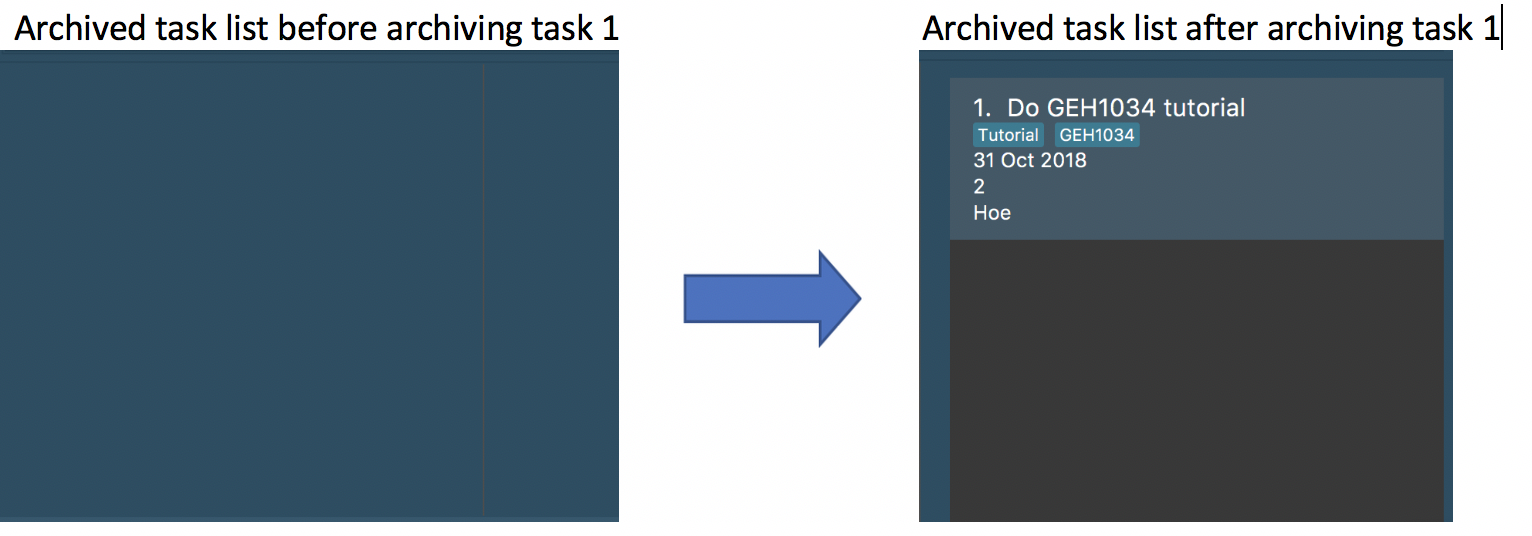
Step 1: archive 1
Below is the screenshot of task list that will appear on screen after step 1.

Step 2: listarchived
Below is the screenshot of archived task list that will appear on screen after step 2.
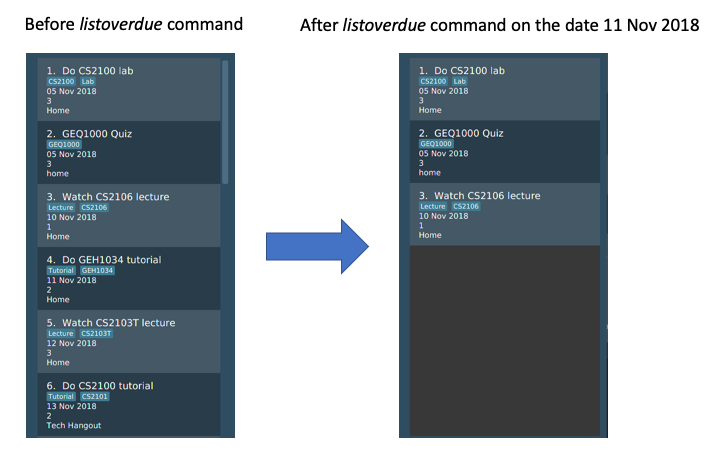
3.9. Viewing Overdue Tasks
Listing all the overdue tasks.
listoverdue
Example:
listoverdue (on the date 111118)
Lists tasks due on 101118 and before.
The following diagram illustrates the SSP before and after listoverdue was entered:
3.11. Viewing Tasks Due This Week
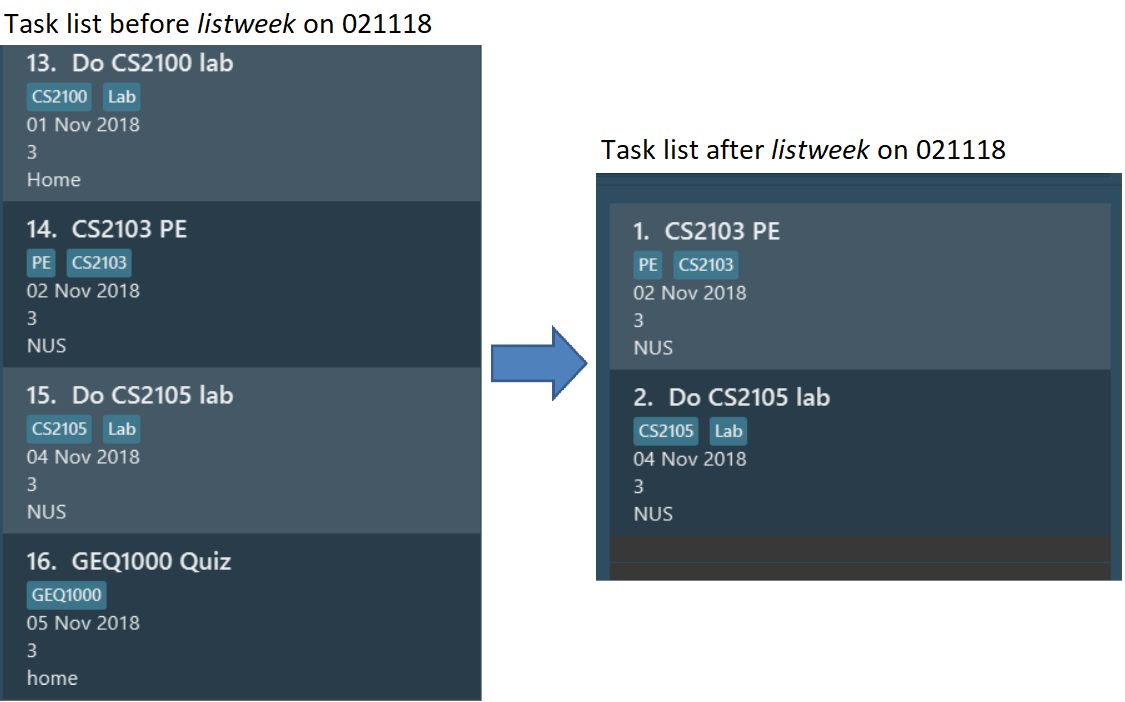
List tasks due from current date till the end of the current week.
listweek
Example:
The following diagram illustrates the SSP when listweek is executed on the date 021118. Only tasks until
041118, which is the closest Sunday, will be displayed.
3.12. Viewing Tasks Due This Month
List tasks due from current date till the end of the current Month.
listmonth
Example:
listmonth (on the date 111118)
Tasks from 111118 to end of the month (301118) are listed.
The following diagram illusatrates the SSP when listmonth is executed on the date 111118. Only tasks until
301118, which is the last day of the month, will be displayed.
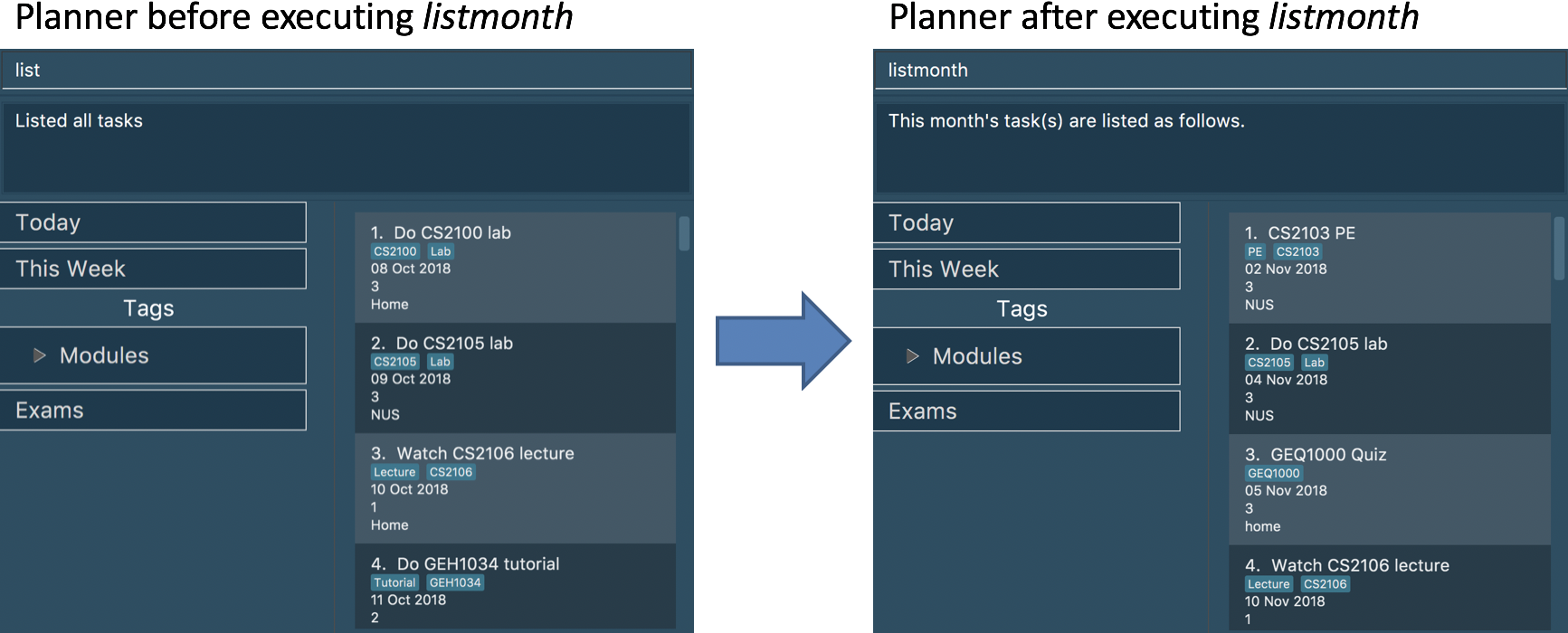
Tasks from 02 Nov '18 to end of the month (30 Nov '18) are listed.
3.13. Viewing Tasks in the Order of Deadline Date and Priority
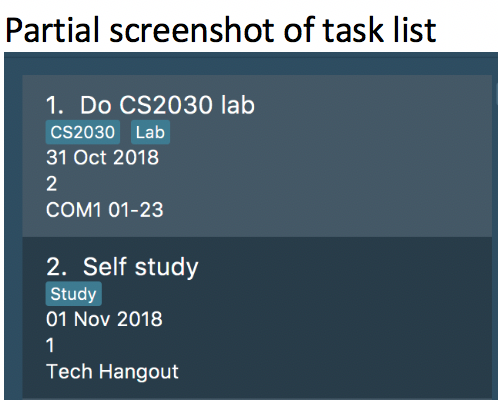
All tasks are automatically loaded in the order of deadlines except for archived tasks.
The order of tasks first depends on deadline date, then priority.
Given below is an example of two tasks with different deadline dates.
Task Do CS2030 lab is listed before task Self study because it has
earlier deadline date.
3.14. Sorting Tasks by Deadline Date and Priority
All tasks are sorted chronologically by default. The order of tasks first depends on deadline date, then priority.
Given below is an example of two tasks with different deadlines.
Task Do CS2030 lab is listed before task Self study because it has
earlier deadline.

If two tasks have the same deadline, then the order depends on priority, one that has
higher priority will appear before one that has lower priority. 3 is the highest priority, while 1 is the lowest.
Given below is an example of two tasks with the same deadline dates.

| Please take note that archived tasks are not shown in order. |
3.15. Finding Tasks by Name
Find tasks whose names match with given keyword. The search is case insensitive, apples and Apples both return
the same tasks. You can include multiple keywords when using find. find CS3230 CS5229 will find all
tasks with name containing CS3230 or CS5229
find NAME
Example:
find tutorial
All tasks with tutorial in their names are listed.
|
The keyword must be whole word. E.g for finding tutorial, tutorial must be used, tut or other variations would not be allowed.
|
The order of the keywords does not matter. For example, find apples buy and find buy apples both return
the
same tasks.You can include multiple keywords when using find. find CS3230 CS5229 will find all tasks with name containing
CS3230 or CS5229.
|
3.16. Filtering Tasks by Tags (Inclusive)
Filter tasks according to tags inclusively. Tags matching ANY of those entered by the user will be listed. The filter
is case insensitive. You may include multiple tags when using filter. For example, filter tutorial quiz project
will return tasks with tags matching at least one of the specified tags.
filter TAG [TAG2] …
Example:
-
filter tutorial
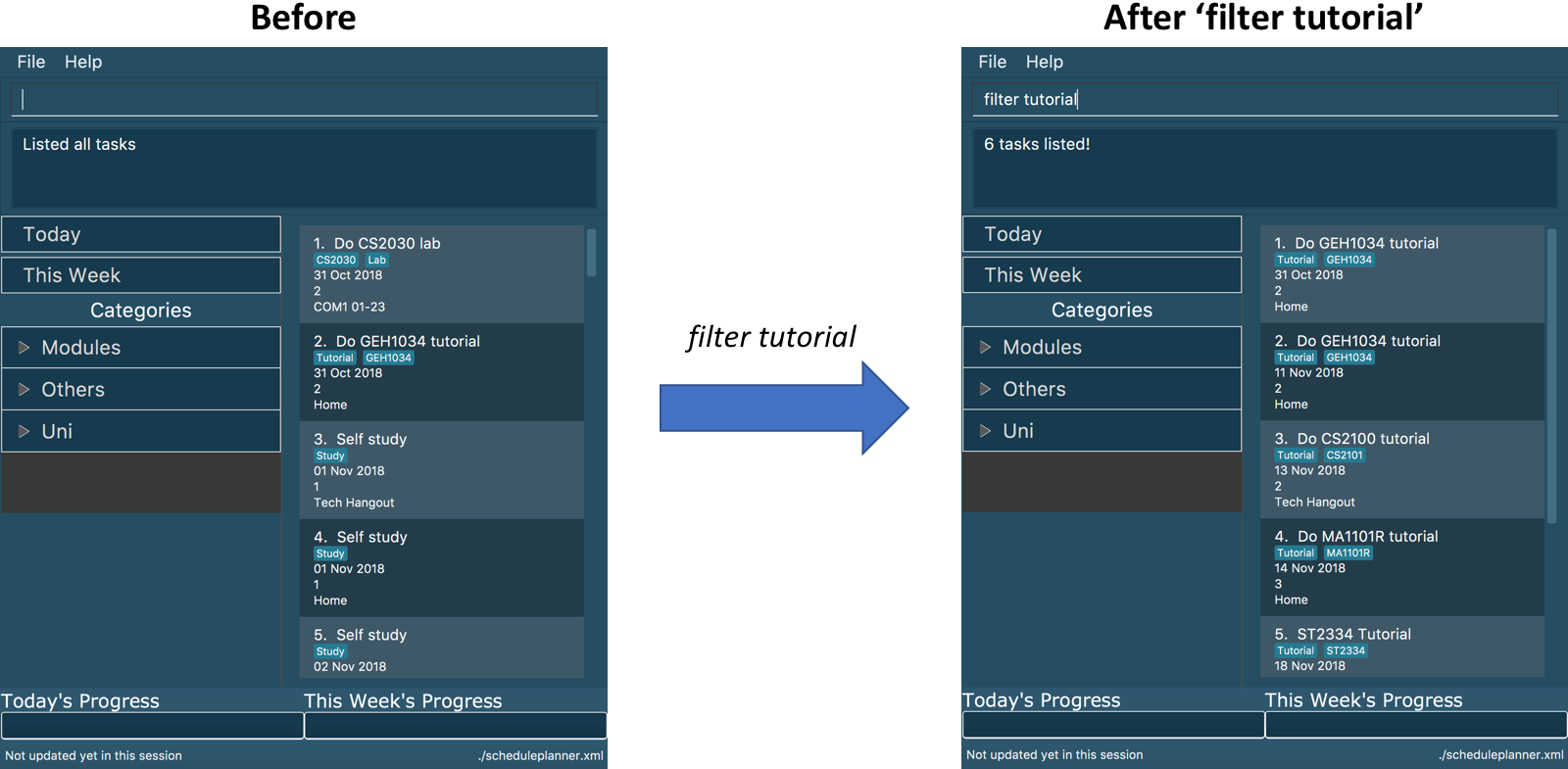
Tasks with the tag tutorial are listed.
The diagram below illustrates the SSP when filter tutorial is executed.

-
filter tutorial cs2100
Tasks with either tutorial, 2100 tags, or both, are listed.
The diagram below illustrates the SSP when filter tutorial cs2100 is executed.
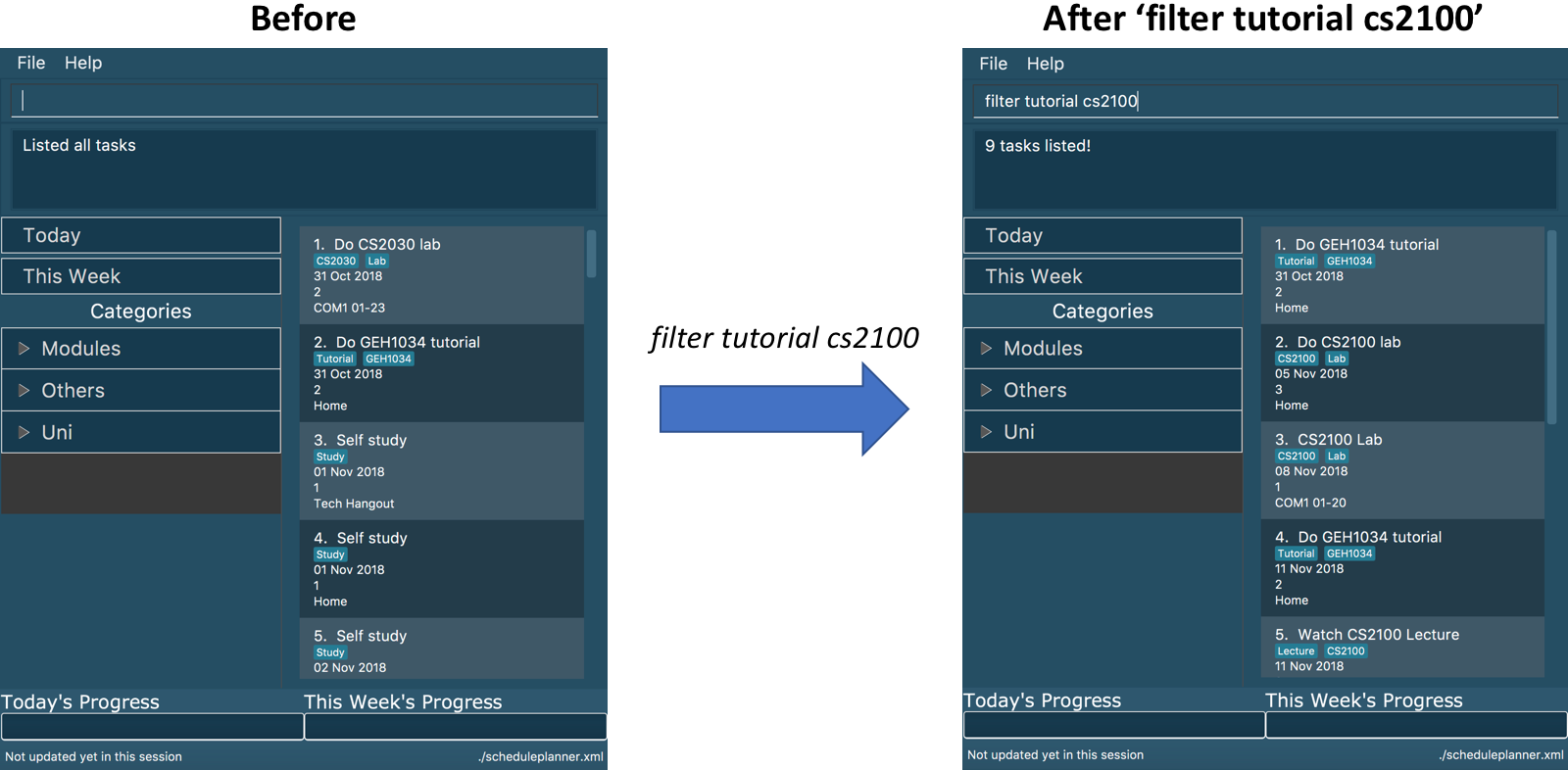
Tasks with either tutorial, 2100 tags, or both, are listed.
|
The keyword must be a whole word. E.g for filtering tutorial, tutorial must be used, tut or other variations would not be allowed.
|
The search is case insensitive. e.g apples matches Apples.
The order of the keywords does not matter. For example, filter tutorial cs2103 and filter cs2103
tutorial both return the same tasks. |
3.17. Filtering Tasks by Tags (Exclusive)
Filter tasks according to tags exclusively. Tags matching ALL of those entered by the user will be listed. The filter
is case insensitive. You may include multiple tags when using filter. For example, filter tutorial quiz project
will return tasks with tags matching ALL of the specified tags.
filterstrict TAG [TAG2] …
Example:
-
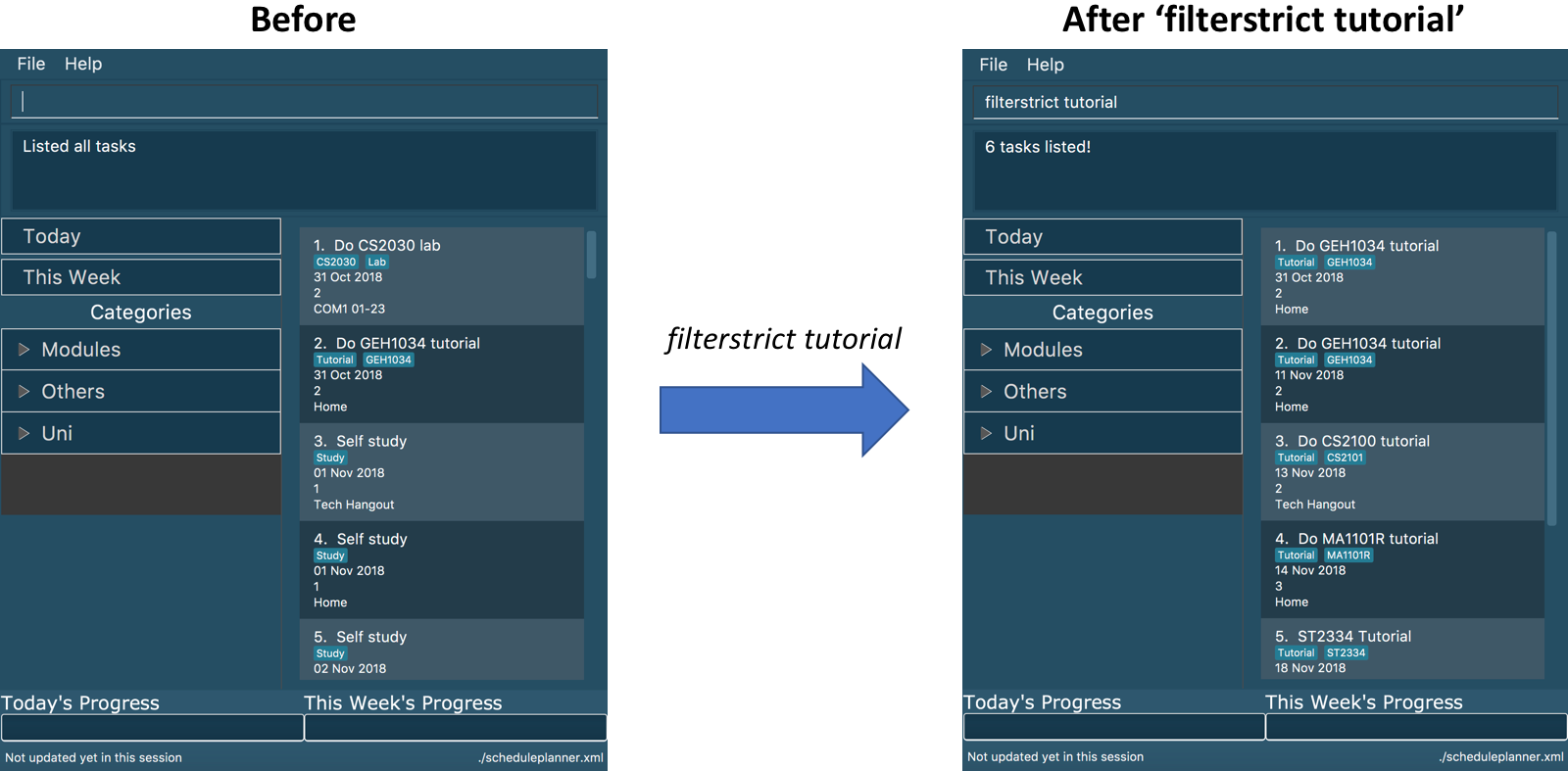
filterstrict tutorial
Tasks with the tag tutorial are listed.
The diagram below illustrates the SSP when filterstrict tutorial is executed.
-
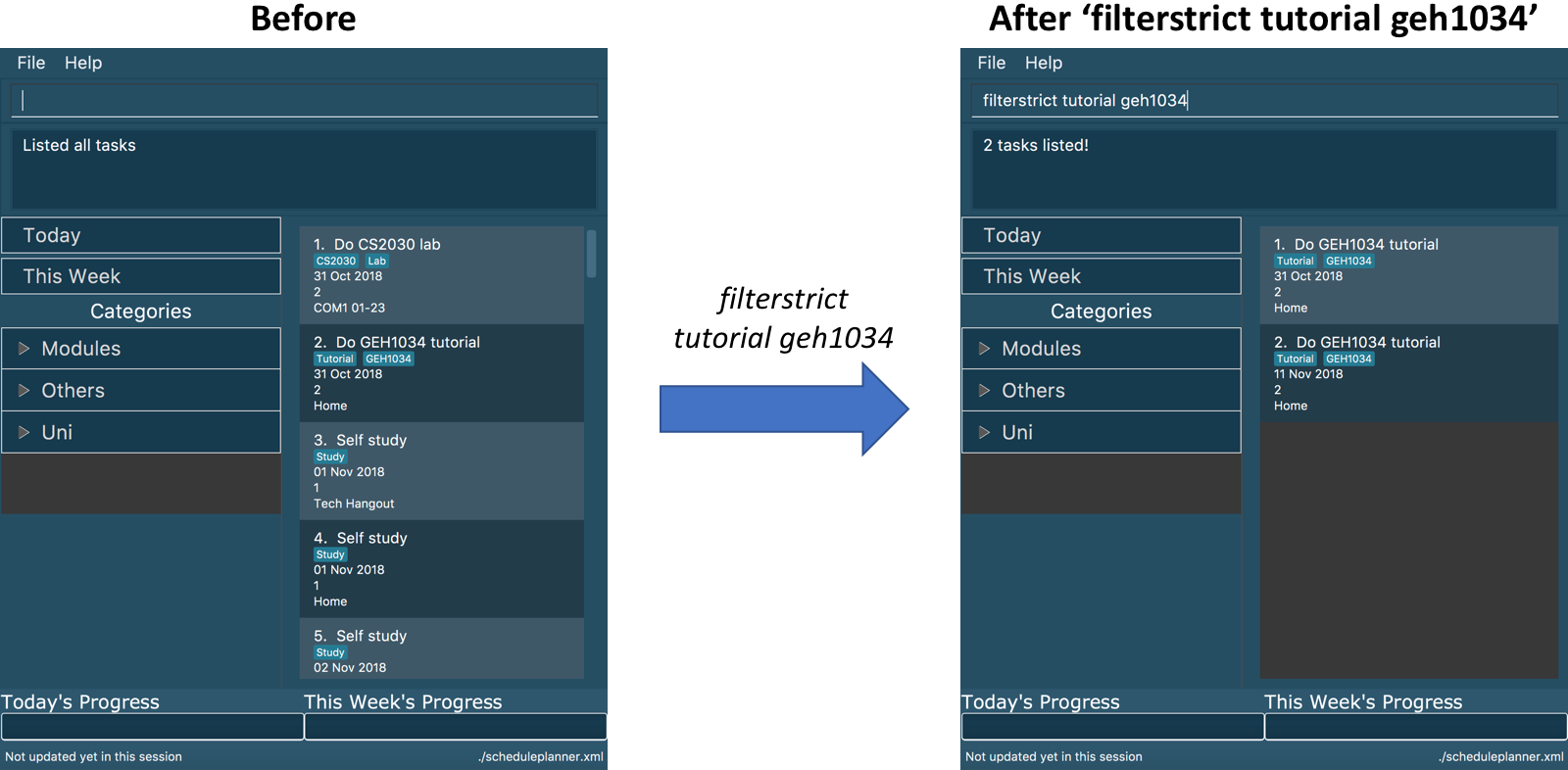
filterstrict tutorial geh1034
Tasks with both tutorial and 2100 tags are listed.
The diagram below illustrates the SSP when filterstrict tutorial geh1034 is executed.
|
The keyword must be a whole word. E.g for filtering tutorial, tutorial must be used, tut or other variations would not be allowed.
|
The order of the keywords does not matter. For example, filterstrict tutorial cs2100 and [blue]`filterstrict
cs2100 tutorial ` both return the same tasks. |
3.18. Generating Academic Calendar
Generate the entire academic calendar based on the first academic day and stores it in storage.
Currently, the generated academic calendar is based on the academic calender of National University of Singapore (NUS). It may not be compatible with academic calendars from other institutions.
Whenever the application is launched within the academic calendar’s dates, the application title will append that
particular week’s description to the title of the application.
firstday DDMMYY
Example:
firstday 130818
The following diagram illustrates when you execute firstday 130818, and launch the application within 121118
- 181118 (Week 13 for NUS academic year 18/19 semester 1), the application title will be appended with "Week 13".
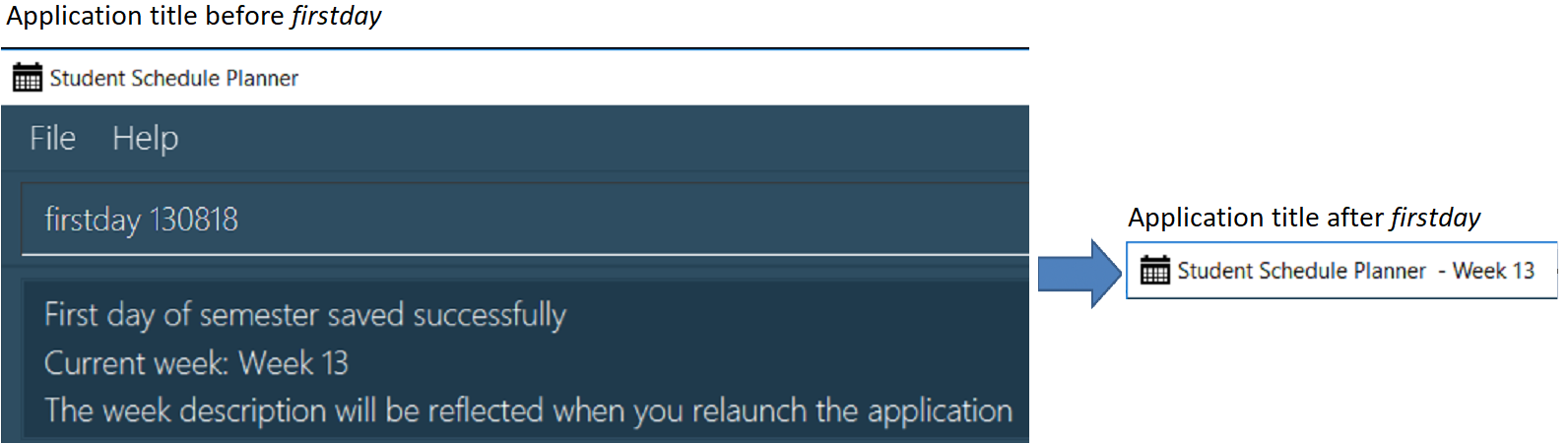
| There would not be any visible changes upon using the command. The changes are only reflected after relaunching the application. |
DDMMYY refers to the date format of day, month and year. It must fulfil the following criteria:
-
DDMMYYmust only be one set of value such as130818. Value such as130818 200818or130818 20will be rejected as they are considered as more than one set of date. -
DDMMYYmust be a valid date within 21st century. -
DDMMYYmust be a Monday.
3.19. Adding a Category
Add a new category to the schedule planner.
You can organize tags by adding tags to relevant categories. For detailed guide about
how to add tags to category, please refer to [Adding a Tag to a Category].
addcat c/CATEGORY
Example:
addcat c/Steam shopping list
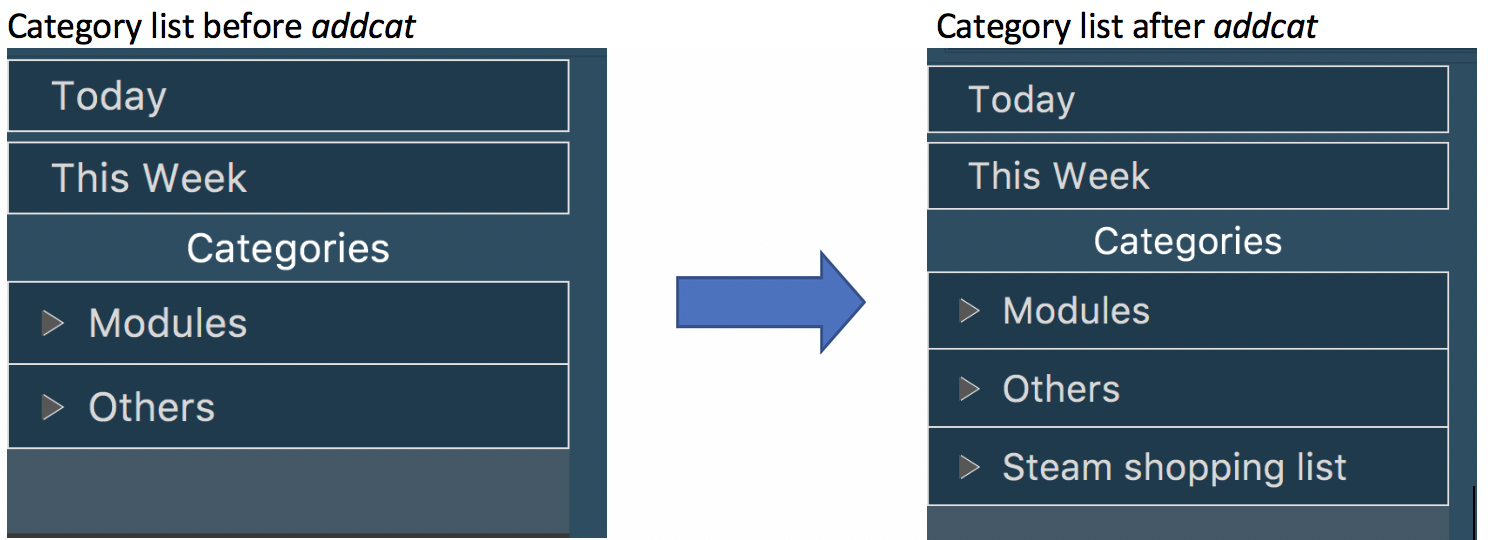
Category name can contain space. For example, Steam, Steam2,
Steam shopping list are all valid category names.
Modules and Others are two categories exist by default.
Please take note that category is case-sensitive. For example, category cats and category Cats are
considered different.
|
| Duplicated categories are not allowed in schedule planner. All categories must have different names. |
All non-default categories (categories except Modules and Others can be removed.
For detailed guide about how to remove categories, please refer to Section 3.22, “Deleting a Category”.
|
All non-default categories (categories except Modules and Others can be renamed.
For detailed guide about how to rename categories, please refer to Section 3.23, “Renaming a Category”.
|
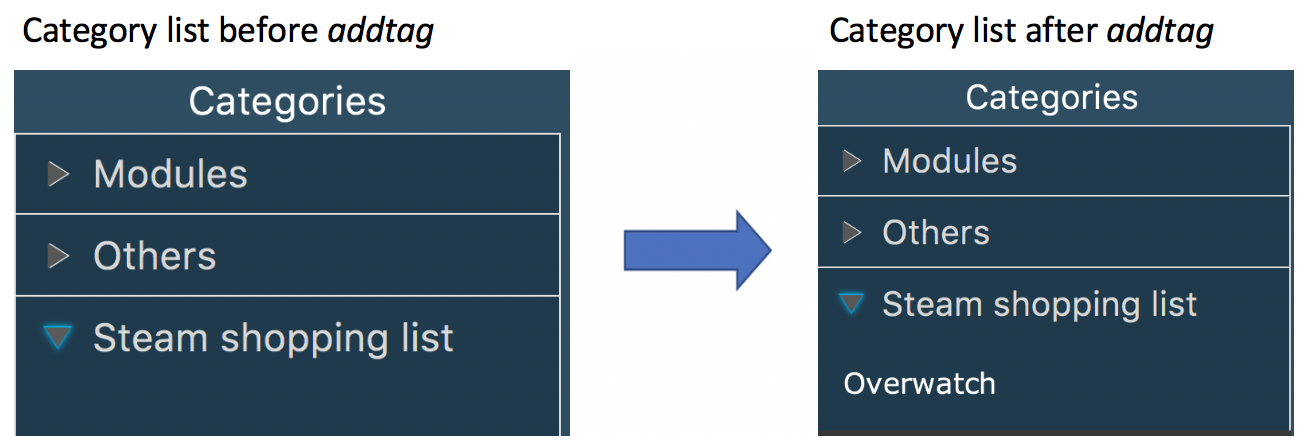
3.20. Adding Tags to Categories
Add a tag to a selected existing category.
addtag c/CATEGORY t/TAG
Example:
addtag c/Steam shopping list t/Overwatch
|
Duplicated tags are not allowed under same category. For instance, in above example, you cannot add another tag Overwatch
to category Steam shopping list. However you can save same tag under multiple categories.
Please take note that naming of tag is case-sensitive. For example, tag name cat and Cat
are considered different.
|
When you add new tasks with new tags (tags that have not been added to any existing categories),
these tags will be automatically added to default category Others.
|
| For how to remove tags from categories, please refer to Section 3.21, “Clearing a Category”. |
3.21. Clearing a Category
Clears all tags saved under selected category. After executing this command, the selected category will not contain any tags.
clearcat c/CATEGORY
Example:
clearcat c/Modules
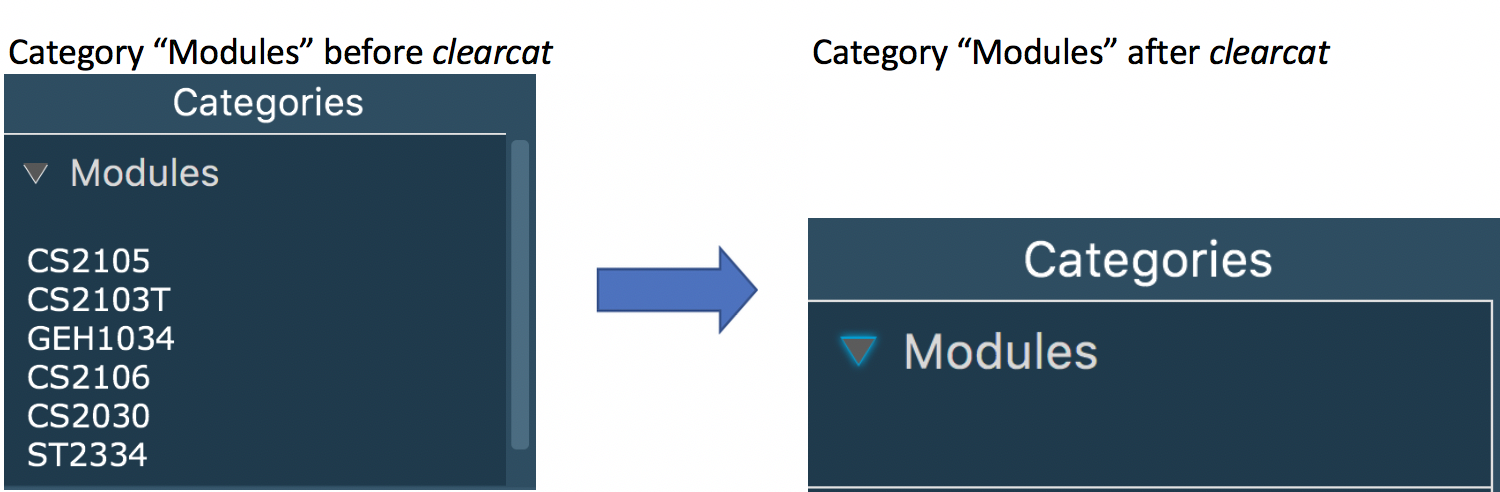
When a category is cleared, tags saved in other categories are not affected.
For instance, in above example, if you have tag CS2105 in category Others
as well, after clearing category Modules, tag CS2105 will still exist in category
Others.
On the other hand, if tag CS2105 is only saved under category Modules, then after clearing
category Modules, the tag CS2105 will be removed from schedule planner.
3.22. Deleting a Category
Delete an existing category from schedule planner.
removecat c/CATEGORY
Example:
removecat c/Steam shopping list
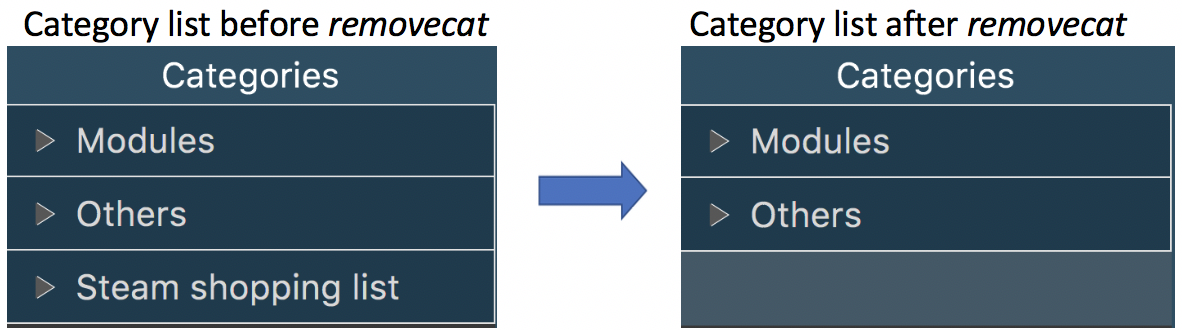
Default categories Modules and Others cannot be removed. The only operation available for default categories is to delete
all tags saved under these two categories.
For more detailed guide about how to do so, please refer to Section 3.21, “Clearing a Category”.
|
3.23. Renaming a Category
Edit the name of an existing category.
editcat c/ORIGINAL CATEGORY NAME c/NEW CATEGORY NAME
Example:
editcat c/Steam shopping list c/Reading list
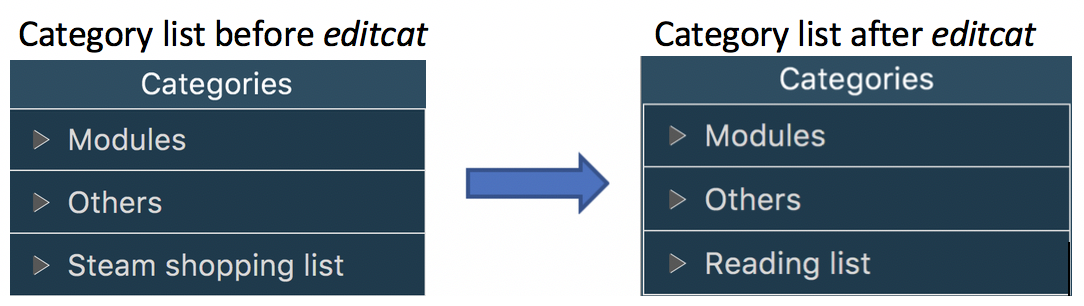
Default categories Modules and Others cannot be renamed.
|
| Duplicated categories are not allowed in schedule planner. Please make sure the new name for selected category does not overlap with other existing categories in your schedule planner. |
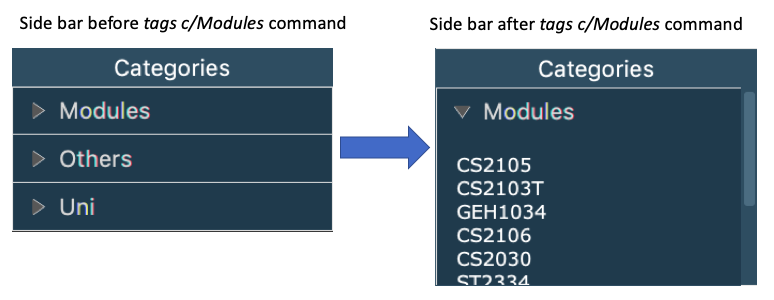
3.24. Displaying Category Tags
Show all tags categorised under the specified category. It expands the tab in the sidebar.
tags c/CATEGORY
Example:
tags c/Modules
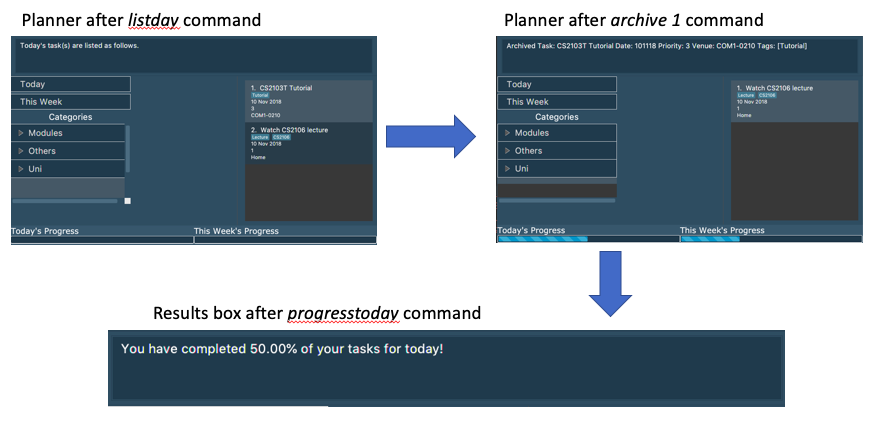
3.25. Displaying Today’s Progress
Show the percentage of tasks archived for the day in the command result box and lists the uncompleted tasks for today
. The progress bar is also displayed at the bottom left of the window.
progresstoday
Example:
Step 1: listday
Step 2: archive 1
Step 3: progresstoday
The diagram below illustrates the SSP after each of the commands entered above.
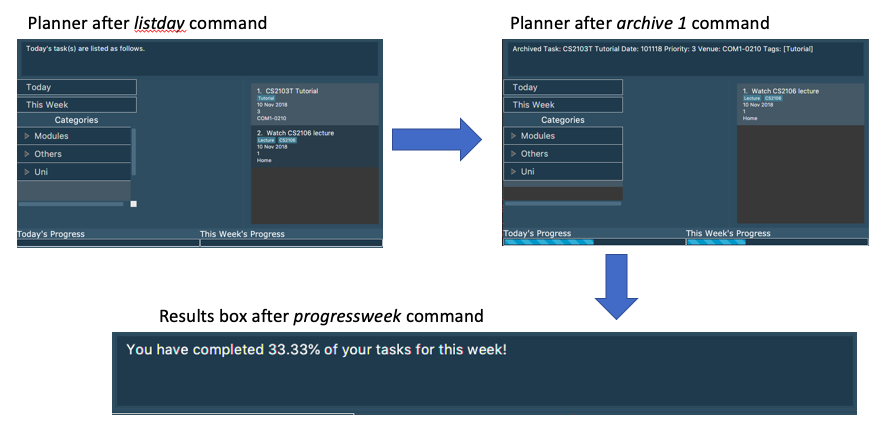
3.26. Displaying This Week’s Progress
Show the percentage of tasks archived from today to the nearest Sunday in the command result box, and lists the
uncompleted tasks from today until the nearest Sunday. The progress bar is also displayed at the bottom right of the
window.
progressweek
Example:
Step 1: listday
Step 2: archive 1
Step 3: progressweek
The diagram below illustrates the SSP after each of the commands entered above.
3.27. Displaying Previous Commands
Show a list of all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order.
history
|
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
3.28. Undoing Previous Command
Restore the schedule planner to the state before the previous undoable command was executed.
undo
Examples:
Step 1: delete 1
Step 2: clear
Step 3: undo (reverses the clear command)
Step 4: undo (reverses the delete 1 command)
Undoable commands are those commands that modify the schedule planner’s content:
-
add -
delete -
edit -
archive -
clear -
addtag -
addcat -
editcat -
removecat -
clearcat
Use the history command to decide if you want to undo the previous undoable command.
|
3.29. Redoing the Previous Undo Command
Reverse the most recent undo command.
redo
Examples:
Step 1: delete 1
Step 2: clear
Step 3: undo (reverses the clear command)
Step 4: undo (reverses the delete 1 command)
Step 5: redo (reapplies the delete 1 command)
Step 6: redo (reapplies the clear command)
3.30. Clearing Schedule Planner
Clear all entries from the schedule planner. Default categories Modules and Others still exists
after the command is executed, but they contain no tags.
clear
3.32. Saving the Data
Data in the Student Schedule Planner is saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
There is no need to save manually.
4. Command Summary
-
Viewing Help :
help
-
Adding Tasks :
add n/NAME p/PRIORITYLEVEL t/[TAG] d/DEADLINE v/VENUE
Example:
add n/do tutorial p/1 t/cs2100 d/121019 v/home
-
Adding Recurring Tasks :
repeat r/REPEATS i/INTERVAL n/NAME p/PRIORITYLEVEL t/[TAG] d/DEADLINE v/VENUE
-
Listing All Tasks :
list
-
Editing a Task :
edit INDEX n/[NAME] p/[PRIORITYLEVEL] t/[TAGS]… d/[DEADLINE]
Example:
edit 3 p/1 d/121019
-
Finding Tasks by Name :
find NAME
Example:
find tutorial
-
Filter Tasks by Tags (Inclusive) :
filter TAG1 [TAG2]…
Example:
filter tutorial …
-
Filter Tasks by Tags (Exclusive) :
filterstrict TAG1 [TAG2]…
Example:
filterstrict tutorial …
-
Deleting Tasks :
delete INDEX
Example:
delete 1
-
Archiving Tasks :
archive INDEX
Example:
archive 1
-
Viewing Archived Tasks :
listarchived
-
Viewing Tasks Due Today :
listday
-
Viewing Tasks Due This Termweek :
listweek
-
Generating Academic Calendar Weeks :
firstday DDMMYY
Example:
firstday 130818
-
Adding a Category:
addcat c/[CATEGORY]
Example:
addcat c/Game list
-
Adding a Tag to a Category:
addtag c/CATEGORY t/TAG
Example:
addtag c/Steam shopping list t/Overwatch
-
Clearing a Category:
clearcat c/CATEGORY
Example:
clearcat c/Modules
-
Deleting a Category:
removecat c/CATEGORY
Example:
removecat c/Steam shopping list
-
Renaming a Category:
editcat c/ORIGINAL CATEGORY NAME c/NEW CATEGORY NAME
Example:
editcat c/Steam shopping list c/Reading list
-
Listing Overdue Tasks :
listoverdue
-
Listing Used Tags :
tags c/CATEGORY
-
Displaying Today’s Progress :
progresstoday
-
Displaying This Week’s Progress :
progressweek
-
Listing Used Commands :
history
-
Undoing previous command :
undo
-
Redoing the Previous Undo Command :
redo
-
Clearing Schedule Planner :
clear
-
Exiting the App :
exit
5. Possible Questions
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous Schedule planner folder.